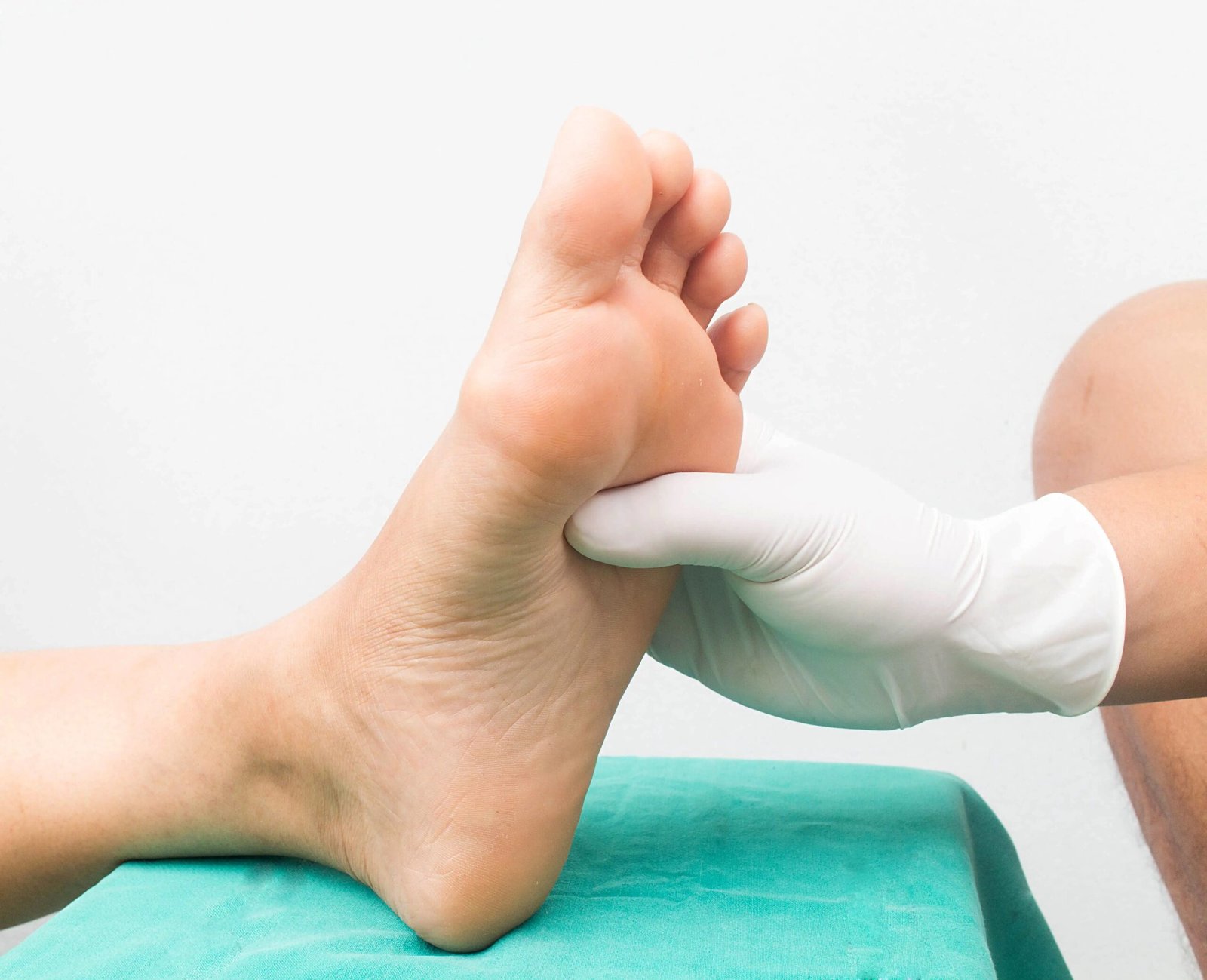
Understanding Diabetic Foot: Diagnosis, Treatment, and PrecautionsDiabetic foot is a serious complication faced by individuals living with diabetes. It arises due to poor blood circulation and nerve damage (neuropathy) in the lower limbs, making the feet vulnerable to infections, ulcers, and, in severe cases, even amputation. Early awareness and medical care can make a substantial difference in managing and preventing this condition.DiagnosisThe diagnosis of diabetic foot involves a comprehensive medical evaluation, including:
-
Physical Examination: Identifying signs like redness, swelling, wounds, ulcers, or skin discoloration.
-
Neuropathy Testing: Using tools such as monofilament or tuning fork to assess nerve sensitivity and function.
-
Circulation Assessment: Employing Doppler ultrasound or Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) tests to evaluate blood flow to the feet.
-
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to detect deeper infections, fractures, or signs of advanced damage.
Treatment OptionsTreating diabetic foot depends on the severity of the condition and typically includes:
-
Wound Care: Cleaning and dressing ulcers to promote healing and prevent infection.
-
Antibiotics: Prescribing oral or intravenous antibiotics for infections.
-
Debridement: Removing dead or infected tissue to allow healthy tissue to regenerate.
-
Revascularization Procedures: Improving blood flow through angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery when circulation is severely compromised.
-
Amputation (as a Last Resort): In cases of untreatable infections or gangrene, amputation may be necessary to protect overall health.
Precautions to Prevent Diabetic FootPrevention plays a vital role in managing diabetic foot. Here are some key precautions:
-
Control Blood Sugar: Keep your diabetes well-managed to reduce complications.
-
Daily Foot Check: Inspect your feet for cuts, sores, or abnormalities.
-
Proper Footwear: Choose comfortable, well-fitted shoes to avoid pressure sores.
-
Hygiene: Wash and dry your feet daily, paying attention to areas between the toes.
-
Avoid Walking Barefoot: Always wear shoes or slippers to minimize the risk of injuries.
-
Regular Medical Check-ups: See a specialist for routine foot examinations and vascular assessments.
![Dr Omar Hamdallah الدكتور عمر نادر يونس حمدالله [Dictation ended]](https://jordanvascular.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/cropped-Untitled-1.png)