Carotid Artery Disease Treatment in Jordan
Carotid Artery Surgery: Latest Techniques for Endarterectomy and Stenting in Jordan
What Is Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease happens when the major blood vessels in your neck (carotid arteries) become narrowed or blocked, usually due to plaque build-up. These arteries supply blood to your brain, so a blockage can lead to a stroke if not treated early.
Signs & Symptoms
Many people with carotid artery disease may not notice symptoms until it becomes serious. However, warning signs may include:
Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
Trouble speaking or understanding speech
Blurred or lost vision in one or both eyes
Dizziness or loss of balance
Treatment Options
Dr Omar Hamdallah offers personalized treatment plans based on the severity of your condition.
Non-Surgical Management:
Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, quitting smoking)
Medications to control blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood thinners
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
Carotid angioplasty and stenting: A tiny balloon is inserted to open the artery, and a stent is placed to keep it open.
Surgical Option:
Carotid endarterectomy: A proven surgical procedure to remove plaque buildup from the artery and restore healthy blood flow.
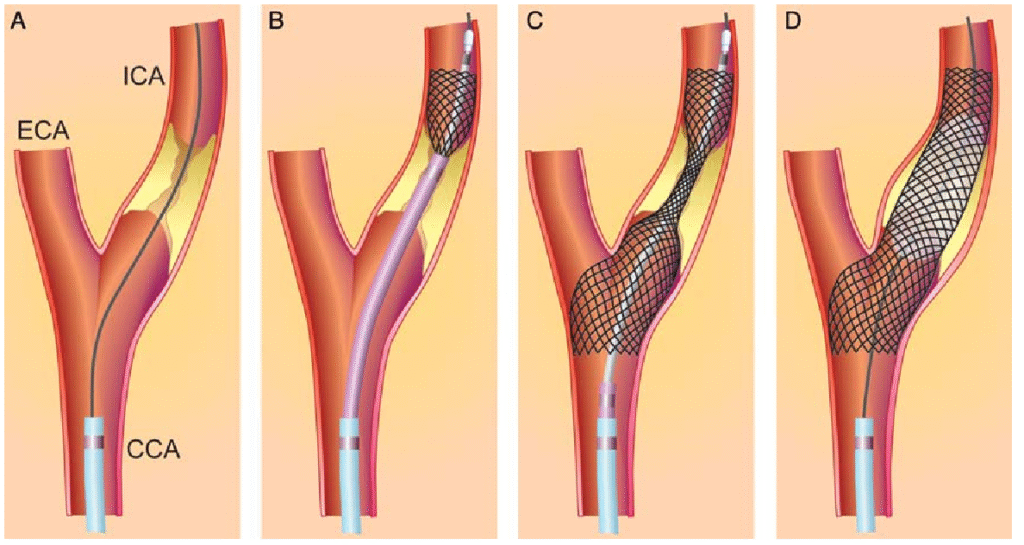
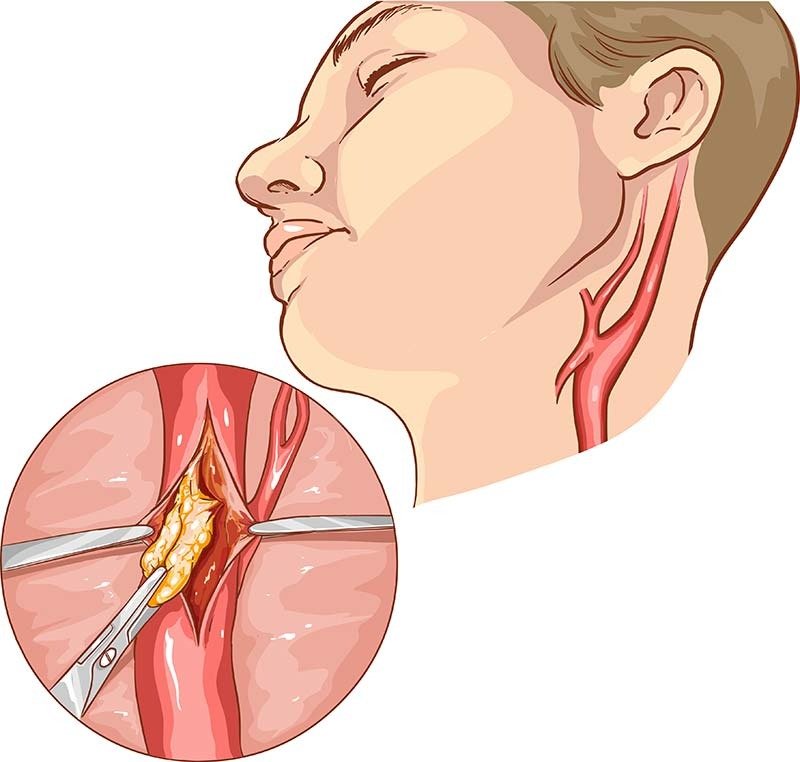
We use advanced Doppler ultrasound and imaging tools to evaluate your carotid arteries in a non-invasive, pain-free way. Our diagnostics are quick, accurate, and done right here in the clinic.
Dr Omar Hamdallah offers personalized treatment plans based on the severity of your condition.
Located in Amman, Jordan, serving patients from across the country.

![Dr Omar Hamdallah الدكتور عمر نادر يونس حمدالله [Dictation ended]](https://jordanvascular.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/cropped-Untitled-1.png)
